johnyradio
Member
Here's a simpler, better question, than my original question .
Will these two sines experience the same percentage power loss on the same wire due to skin effect (passed separately, not at the same time) .
Vertical axis is voltage .
question as previously stated (ignore):
Assume a wire has a given skin effect depth at a particular frequency.
Compare the following scenarios:
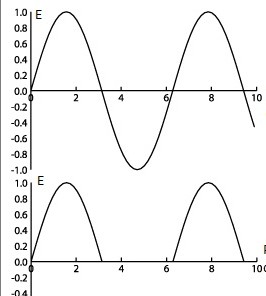
Scenario 1: One such wire. We send a bipolar AC current at that frequency, at a particular peak to peak voltage amplitude down that wire. Due to skin effect, it will have a particular impedance, and thus a particular power loss.
Scenario 2: Same such wire, identical to the above wire. Identical AC current. Except, we're sending the positive half ONLY down the wire. Ie, half rectified.
Will the 2nd scenario suffer the same power loss (due to skin effect) as the 1st scenario? As a percentage of the original, not as absolute amps.
Here are the two scenarios:

Or, as sine:
Will these two sines experience the same percentage power loss on the same wire due to skin effect (passed separately, not at the same time) .
Vertical axis is voltage .

question as previously stated (ignore):
Assume a wire has a given skin effect depth at a particular frequency.
Compare the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: One such wire. We send a bipolar AC current at that frequency, at a particular peak to peak voltage amplitude down that wire. Due to skin effect, it will have a particular impedance, and thus a particular power loss.
Scenario 2: Same such wire, identical to the above wire. Identical AC current. Except, we're sending the positive half ONLY down the wire. Ie, half rectified.
Will the 2nd scenario suffer the same power loss (due to skin effect) as the 1st scenario? As a percentage of the original, not as absolute amps.
Here are the two scenarios:

Or, as sine:
Last edited:

