Since the response to these posts has been underwhelming, I will continue 
Often, it is necessary to interface 5 volt and 3.3 volt systems; a sensor may not be 5 volt tolerant, but other parts of the system may need to run at 5 volts. This bi-directional level shifter circuit may be used for I2C and SPI interfaces or general digital I/O. It uses only one mosfet and two resistors (per channel), so it needs a very small footprint on a pcb.
The first reference explains this circuit. The second covers this circuit but goes on to explain alternatives where is necessary to isolate an unpowered bus section and other advanced cases.
NXP Application Note AN10441: Level shifting techniques in I2C-bus design
Phillips Application Note AN97055: Bi-directional level shifter for I²C-bus and other systems
If you find these posts useful, a comment or like would be appreciated.
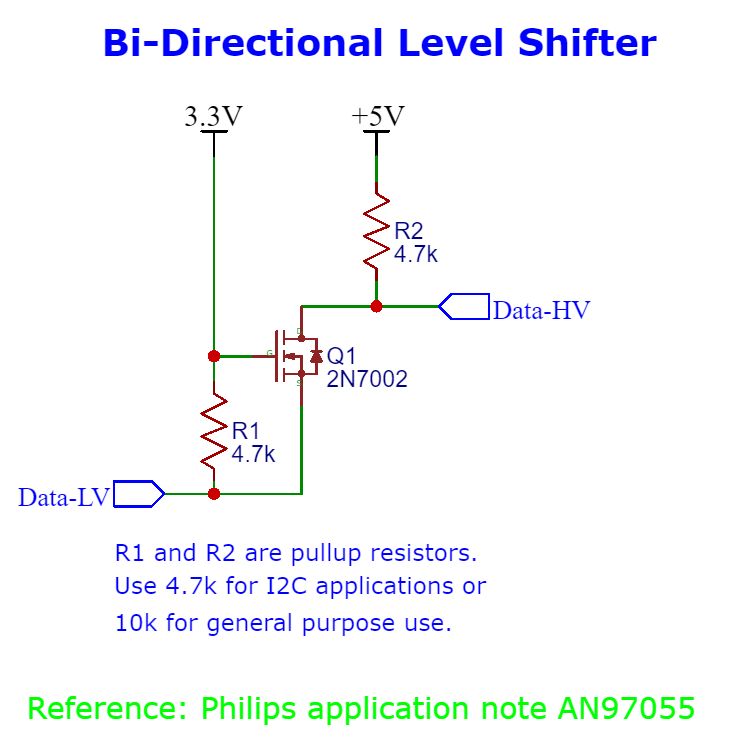
Often, it is necessary to interface 5 volt and 3.3 volt systems; a sensor may not be 5 volt tolerant, but other parts of the system may need to run at 5 volts. This bi-directional level shifter circuit may be used for I2C and SPI interfaces or general digital I/O. It uses only one mosfet and two resistors (per channel), so it needs a very small footprint on a pcb.
The first reference explains this circuit. The second covers this circuit but goes on to explain alternatives where is necessary to isolate an unpowered bus section and other advanced cases.
NXP Application Note AN10441: Level shifting techniques in I2C-bus design
Phillips Application Note AN97055: Bi-directional level shifter for I²C-bus and other systems
If you find these posts useful, a comment or like would be appreciated.
